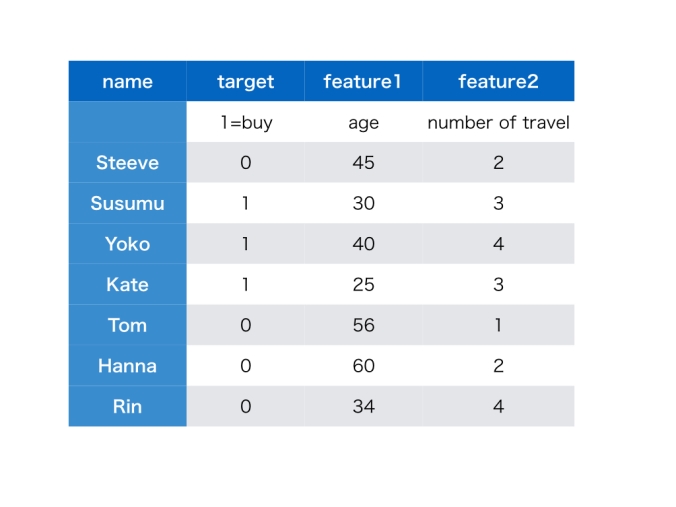
In July, I have researched TensorFlow, which is a deep learning library by Google, and performed several classification tasks. Although it is open-source software and free for everyone, its performance is incredible as I said in my last article.
When I perform image classification task with TensorFlow, I found that computers can see our world better and better as deep learning algorithms are improved dramatically. Especially it is getting better to extract “features“, what we need to classify images.
Images are just a sequence of numbers for computers. So some features are difficult for us to understand what they are. However computers can do that. It means that computers might see what we cannot see in images. This is amazing!
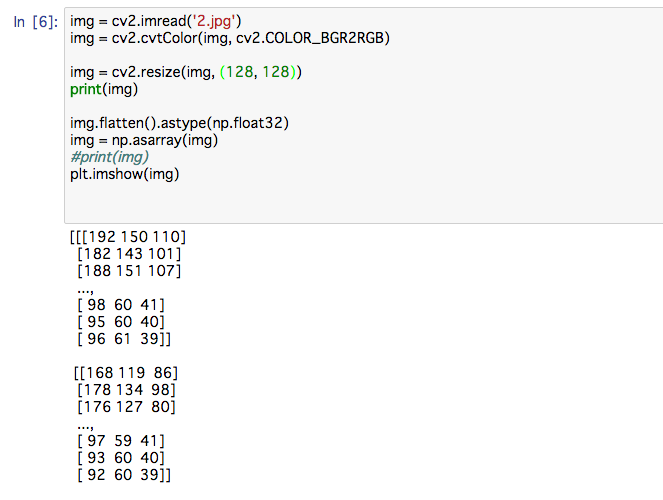

This is an example “how images are represented as a sequence of numbers. You can see many numbers above (These are just a small part of all numbers). These numbers can be converted to the image above which we can see. But computers cannot see the image directly. It can only see the image through numbers above. On the other hand, we can not understand the sequence of numbers above at all as they are too complicated. It is interesting.
In marketing, when images of products are provided, computers might see what are needed to improve the products and to be sold more. Because computers can understand these products more in a deferent way as we do. It might give us new way to consider marketing strategy. Let us take T shirts as an example. We usually consider things like color, shape, texture, drawings on it, price. Yes, they are examples of “features” of T shirts because T-shirts can be represented by them. But computers might think more from the images of T shirts than we do. Computers might create their own features of T-shirts.
Then, I would like to point out three things to consider new marketing strategy.
1.Computers might extract more information that we do from same images.
As I explained, computers can see the images in a different way as we do. We can say same things for other data, such as text or voice mail as they are also just a sequence of numbers for computers. Therefore computers might understand our customers behavior more based on customer related data than we do when deep learning algorithms are much improved. We sometimes might not understand how computers can understand many data because computers can understand text/speech as a sequence of numbers and provide many features that are difficult to explain for us.
2.Computers might see many kind of data as massive amount data generated by costomers
Not only images but also other data, such as text or voice mail are available for computers as they are also just a sequence of numbers for computers. Now everything from images to voice massages is going to digital. I would like to make computers understand all of them with deep learning. We cannot say what features are used when computers see images or text in advance. But I believe some useful and beneficial things must be found.
3. Computers can work in real-time basis
As you know, computers can work 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. Therefore it can operate in real-time basis. When new data is input, answer can be obtained in real-time basis. This answer can be triggered next actions by customers. These actions also can be recorded as digital and fed to into computers again. Therefore many digital data will be generated when computers are operated without stop /rest time and the interactions with customers might trigger chain-reactions. I would like to call it “digital on digital”
Images, social media, e-mails from customers, voice mail, sentences in promotions, sensor data from customers are also “digital”. So there are many things that computers can see. Computers may find many features to understand customer behaviors and preferences in real-time basis. We need to have system infrastructures to enable computers to see them and tell the insight from them. Do you agree with that?
Notice: TOSHI STATS SDN. BHD. and I do not accept any responsibility or liability for loss or damage occasioned to any person or property through using materials, instructions, methods, algorithm or ideas contained herein, or acting or refraining from acting as a result of such use. TOSHI STATS SDN. BHD. and I expressly disclaim all implied warranties, including merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. There will be no duty on TOSHI STATS SDN. BHD. and me to correct any errors or defects in the codes and the software.